

Mexico 100 Pesos 1981 UNC
Front: Venustiano Carranza, painting by Jose Clemente Orozco
Back: Tula, Hidalgo Chac Mool statue at Chichen Itza
The Chac-Mool depicts a human figure in a position of reclining with the head up and turned to one side, holding a tray over the stomach. The meaning of the position or the statue itself remains unknown. Chac-Mool statues are found in or around temples in Toltec , in post-Classic Maya civilization sites with heavy Toltec influence, such as Chichen Itza. Chac-Mools can be found throughout Central Mexico and Yucatán. In addition to Tula and Chichen Itza, sites known for Chac-Mools include Mexico City, Cempoala, Tlaxcala, and Quiriguá in Guatemala.
Read more Venustiano Carranza de la Garza (December 29, 1859 – May 21, 1920) was one of the leaders of the Mexican Revolution. He ultimately became President of Mexico following the overthrow of the dictatorial Huerta regime in the summer of 1914 and during his administration the current constitution of Mexico was drafted. He was assassinated near the end of his term of office at the behest of a cabal of army generals resentful at his insistence that his successor be a civilian.

President Carranza in Piedras Negras, Coahuila in 1915.

Bernardo Reyes (1850-1913), Porfirio Díaz's "man in the north". Carranza formed a personal friendship with Reyes, and Reyes' patronage was responsible for Carranza's election to the Mexican Congress in 1898. Information and Image Obtained From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia




 President Carranza in Piedras Negras, Coahuila in 1915.
President Carranza in Piedras Negras, Coahuila in 1915. Bernardo Reyes (1850-1913), Porfirio Díaz's "man in the north". Carranza formed a personal friendship with Reyes, and Reyes' patronage was responsible for Carranza's election to the Mexican Congress in 1898. Information and Image Obtained From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Bernardo Reyes (1850-1913), Porfirio Díaz's "man in the north". Carranza formed a personal friendship with Reyes, and Reyes' patronage was responsible for Carranza's election to the Mexican Congress in 1898. Information and Image Obtained From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia








 Gandhi on the Salt March
Gandhi on the Salt March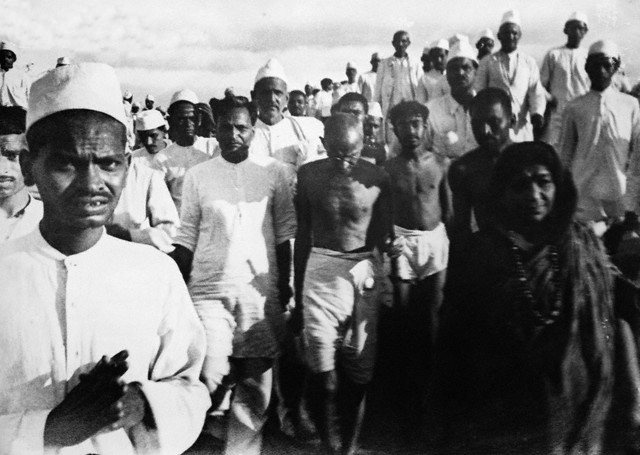 Gandhi on the Salt March, Sarojini Naidu on the right.
Gandhi on the Salt March, Sarojini Naidu on the right.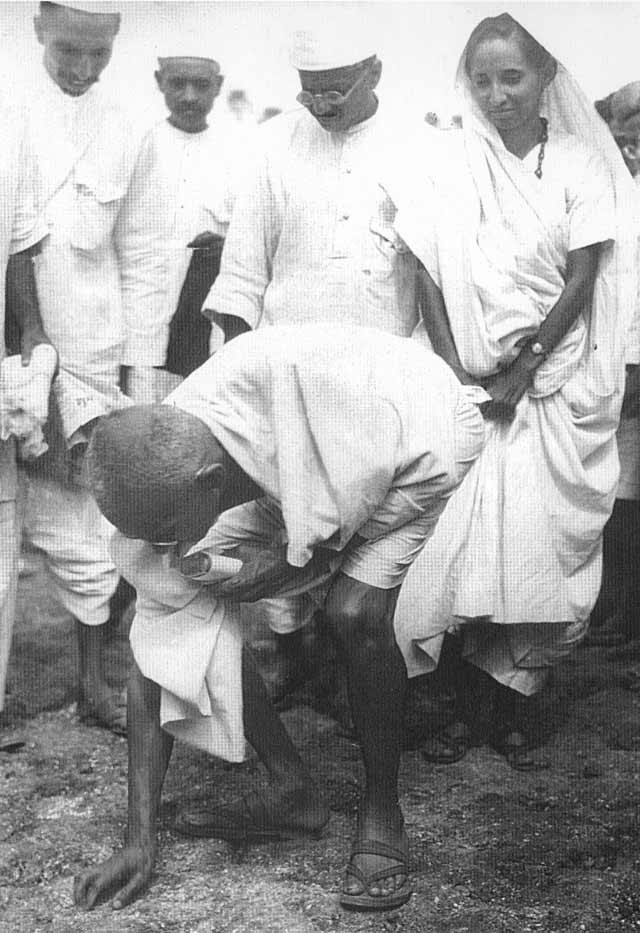 Gandhi at Dandi, April 5, 1930, picking up a lump of salty mud.
Gandhi at Dandi, April 5, 1930, picking up a lump of salty mud.